Converting a Tertiary Alcohol to a Secondary Alcohol
Oxidoreductases Transferases Hydrolases Lyases somerases Ligases 2 Name the enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of phosphate groups. The correct option is B.
Alcohol Oxidation Strong Weak Oxidants Master Organic Chemistry
A new method to convert secondary alcohols in their single mirror image form into tertiary alcohols has been developed.
. A wide range of highly functionalized chiral tertiary alcohols has been obtained in high to excellent yields with excellent enantioselectivities. Reacting a Grignard reagent with any other aldehyde will lead to a secondary alcohol. The conversion usually requires a two-step sequence involving the conversion of alcohols into leaving groups such as halides and sulfonate esters followed by reduction with metal hydrides such as LiAlH4 LiHBEt3 Bu3SnH radical initiator.
If instead of starting with propyl. The resulting product would have been a tertiary alcohol. CLASSES AND TRENDING CHAPTER.
It is a very convenient reaction for unfunctionalized primary secondary and tertiary alcohols. With Lucas reagent 2-propanol secondary alcohol gives a turbidity around five minutes. Methyl and primary alcohols are converted to alkyl halides via S N 2 reaction according to the general mechanism shown below.
The success of this strategy relies on the. But 1-propanol primary alcohol does not a turbity with Lucas reagent. Secondary tertiary allylic and benzylic alcohols appear to react by a mechanism that involves the formation of a carbocation in an S_N1 reaction with the protonated alcohol acting as the substrate.
View solution View more. 3 Pepsin is a protease that is active in the stomach with an optimal pH of 15-20. One is increasing number of carbon atoms or producing a primary alcoholSecond methods is limited to very few secondary alcohols because it is difficulat to convert a secondary alcohol to a primary alcohol.
Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alcohols with either lithium aluminum hydride LiAlH 4 or sodium borohydride NaBH 4. So according tothe time this turditity is given 1. First let us understand the structure of primary alcohols and secondary alcohols.
Complete step by step solution. Ketone is the intermediate functional group which is formed in the conversion of secondary alcohol to the tertiary alcohol. This test readily distinguishes between primary secondary and tertiary alcohol based on whether a reaction occurs and on the reaction time.
Then secondary alcohol is treated with aqueous. These reactions result in the net addition of the elements of H 2 across the CAO bond. The presence of this OH cluster permits the alcohols within to form H-bonds with their neighboring atoms.
Identify the tertiary alcohols. Fluorination of alcohols is also possible and can be achieved by the reactions of. Tertiary alcohol doesnt get oxidized in the presence of sodium dichromate.
As these examples illustrate reduction of an aldehyde gives a primary alcohol and reduction of a ketone gives a secondary alcohol. The S_N1 mechanism is illustrated by the reaction tert-butyl alcohol and aqueous hydrochloric acid H_3O Cl-. Secondary alcohol gets easily oxidized to ketone but further oxidation is not possible.
Finally reacting a Grignard reagent with a ketone will generate a tertiary alcohol. Tertiary alkyl halides are made using the two-step S N 1 mechanism that occurs via a carbocation intermediate which is stabilized by hyperconjugation. To produce a primary alcohol the Grignard reagent is reacted with formaldehyde.
In the second method you can convert secondary alcohol to an alkyl halide compound. Secondary alcohols will dehydrate at. Conversion of alcohols into iodides using potassium iodide in a phosphoric acidphosphorus pentoxide mixture is a well-established transformation in organic chemistry.
Class 5 The Fish Tale Across the Wall Tenths and Hundredths Parts and Whole Can you see the Pattern. However for primary alcohols the protonation of the hydroxyl group leads to the concerted S N 2 route. When the iodide is treated with moist silver oxide the iodine atom is replaced by a hydroxyl group according to the general method 1 above thus yielding a secondary alcohol.
Dehydration with conc phosphoric acids results in. View solution The general formula of primary secondary and tertiary alcohol respectively are. You know primary alcohols and secondory alcohols answer in different way to Lucas reagent anhydrous ZnCl 2 concentrated HCl.
One may also ask how do you convert primary alcohol to tertiary alcohol. The I and Br are strong enough nucleophiles to attack the primary carbon and the OH 2 in turn is an excellent leaving group in form of neutral water molecule. The overall process involves removing the hydrogen atom attached to carbon of the secondary alcohol and effectively replacing it with an alkyl alkenyl or aryl group.
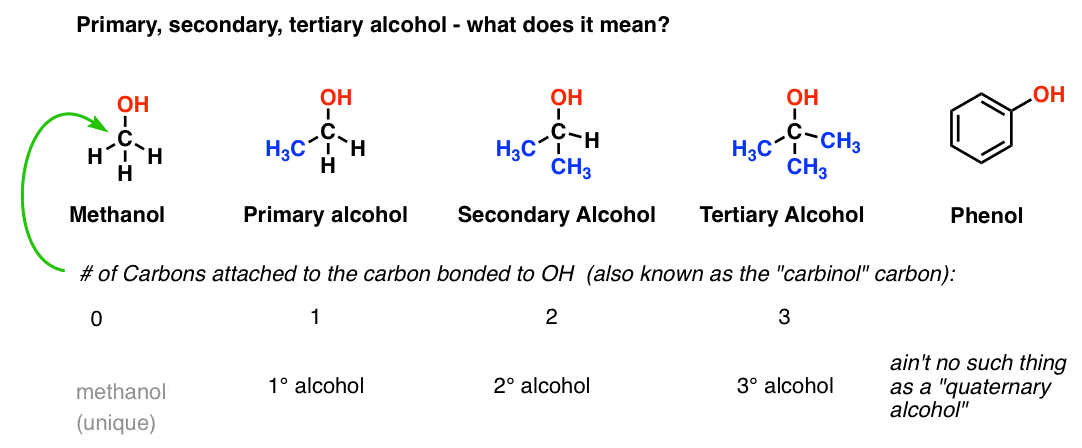
Explain the mechanism of converting primary alcohol to secondary alcohol. Tertiary alcohols are the units that feature hydroxyl radicals hooked up to the atom that is connected to 3-radical groups. The names of the alcohol are derived according to the alkane backbone.
HCl is the weakest acid among these and Cl is not a strong nucleophile so the. Secondary alcohols can proceed via either mechanism based on the reaction conditions. Its physical properties chiefly rely upon its structures.
Furthermore starting from a single mirror image form of the secondary alcohol either mirror image form of the tertiary alcohol can be made with high levels of stereocontrol. 1 Which of the following classes of enzymes would be used to convert a tertiary alcohol into a secondary alcohol. CH3 CHICH3 AgOH CH3CH OHCH3 Agl.
The general method involves the oxidation of the alcohol and then the oxidation product is reacted with organometallic reagents such as Grignard reagent to get the secondary alcohol. Enzymes that consist of quaternary structures with slight variations in the amino acids in the poly peptide sub-units but catalyze the same chemical reaction Lyase addition of water to a double bond Oxidoreductase removing hydrogen atoms Hydrolase splitting peptide bonds in proteins Isomerase converting a tertiary alcohol to a secondary alcohol. Thus the rate of oxidation upon oxidation with sodium dichromate helps us in the identification of primary secondary and tertiary alcohol.
The bonds make the.
Alcohols 1 Nomenclature And Properties Master Organic Chemistry
Alcohol Oxidation Strong Weak Oxidants Master Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Lessons
Hsc Chemistry Module 7 Inquiry Question 4
Alcohols 1 Nomenclature And Properties Master Organic Chemistry Chemistry Science Chemistry Chemical Bond

0 Response to "Converting a Tertiary Alcohol to a Secondary Alcohol"
Post a Comment